ICEECE2012 Poster Presentations Obesity (114 abstracts)
Association between metabolic syndrome and serum leptin level in postmenopausal women
S. Lee & Y. You
The Catholic University of Korea, Suwon, Republic of Korea.
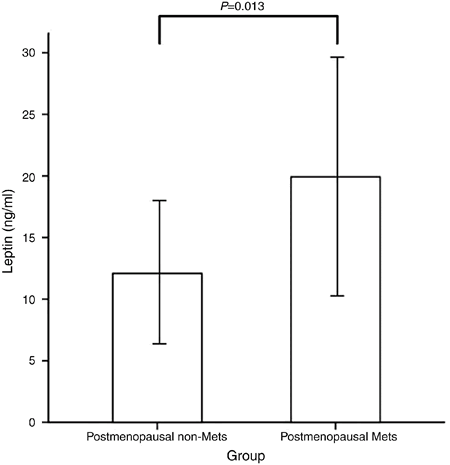
Menopausal status is associated with weight gain, increased central fat mass, abnormal lipid metabolism, insulin resistance, and susceptibility to metabolic syndrome (MetS). Leptin is synthesized and secreted by adipocytes. Serum leptin levels are highly correlated with fat mass. We determined the association between MetS and serum leptin levels in 153 postmenopausal women. The difference in serum leptin level between MetS and non-MetS groups showed a statistical significance after adjusting for body mass index (BMI; 19.9±9.5 vs 12.1±5.9 ng/ml, P=0.013). The indicator of abdominal obesity, waist-to-hip ratio (WHR) and visceral fat area (VFA), had a positive correlation with serum leptin level in non-obese subjects after adjusting for BMI (P=0.017, P<0.001 respectively). Of the components of MetS, abdominal obesity and the number of MetS components had a positive correlation with serum leptin level (P<0.05, P<0.001 respectively). In conclusion, our study showed that serum leptin was associated with MetS independent of BMI. The increase in prevalence in MetS in postmenopausal women may increase the risk of CVD; therefore, the prevention and treatment of MetS are important. Further researches are needed to investigate the additional direct and indirect mechanisms of action of leptin associated with MetS and to clarify the role of leptin on MetS.
Mean leptin levels in non-MetS and MetS groups. After adjustment for BMI, the difference of leptin between two groups showed a statistical significance (P=0.013). P value was calculated by ANCOVA.
Declaration of interest: The authors declare that there is no conflict of interest that could be perceived as prejudicing the impartiality of the research project.
Funding: This research did not receive any specific grant from any funding agency in the public, commercial or not-for-profit sector.
| A1 | A2 | |
| WHR | 0.610* | 0.213* |
| Total triglyceride (mg/dl) | 0.270* | 0.163 |
| HDL cholesterol (mg/dl) | -0.254* | -0.111 |
| FPG (mg/dl) | 0.137 | 0.080 |
| SBP (mmHg) | 0.302* | 0.004 |
| DBP (mmHg) | 0.332* | 0.083 |
| WHR, waist-to-hip ratio; HDL, high-density lipoprotein; FPG, fasting plasma glucose; SBP, systolic blood pressure; DBP, diastolic blood pressure. *P<0.05. | ||
 }
}



