ICEECE2012 Poster Presentations Diabetes (248 abstracts)
Resource utilization and patient satisfaction associated with switching insulin in Greece (Subanalysis of the SWING study).
K. Aloumanis 1 , N. Tentolouris 2 , M. Reaney 3 , C. Dafni 1 & V. Drossinos 1
Eli Lilly & Co Ltd, Surrey, United Kingdom.
Purpose: Diabetic patients (T2D) switch from short-acting insulin to rapid-acting analogue (H-A) and less commonly from A-H. The SWING study was designed to assess treatment costs, glucose control, satisfaction, and quality of life in T2D following H-A or A-H switches.
Methods: SWING was a multinational, prospective, observational study of previously mentioned parameters associated with switching in either direction between any rapid-acting analogue insulin therapy and short-acting human insulin therapy over 12 months following the switch. Data were collected at baseline (switch) and at approximately 3, 6 and 12 months post-switch. Descriptive analysis of the Hellenic subgroup data is presented.
Results: 309 Greek patients switched H-A [N=270, mean(SD) age 65.3(11.9), Body Mass Index (BMI) 28.8(4.5) kg/m2, diabetes duration 15.6(9.0) years] or A-H [N=39, age 64.4(12.6), BMI 28.8(5.4) kg/m2, diabetes duration 13.7(7.9) years] insulin.
Mean (SD) HbA1c at baseline was 8.4(1.3) % (H-A) and 8.4(1.4)% (A-H) respectively and decreased over 12 months: −1.2(1.1) units H-A, −1.3(1.3) units A-H.
Reported hypoglycaemia incidence (recalled over the 6 months preceding baseline) was 45.9% for H-A and 28.2% for A-H.
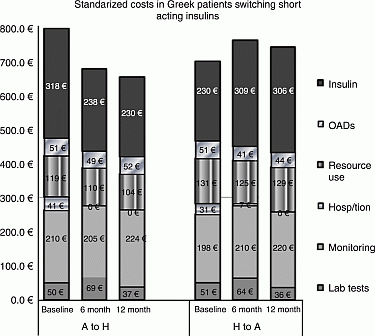
Mean (SD) direct diabetes-related costs for standardized 6 month periods prior to switch, 0–6 months and 6–12 months following switch were €692.2(293.1), €755.3(235.7) and €734.6 (231.9) for H-A, and €788.9(402.0), €670.5(170.0) and €646.8(171.5) for A-H respectively. Compared to baseline, intra-patient standardised costs at 0–12 months post switch were mean (SD) €31.0(257.9) higher in H-A (n=246) and €168.6(342.2) lower in A-H (n=36).
Conclusions: In a cohort of Greek diabetic patients switching short-acting insulin A-H, total mean direct costs were lower in the 6–12 month period post-switch than in the 6 month period prior to the switch, although standard deviations are wide. Mean HbA1c decreased following switch in both groups. Substantially more patients were switched to analogues. Results should be interpreted in the context of an observational study.
Declaration of interest: I fully declare a conflict of interest. Details below.
Funding: This work was supported, however funding details unavailable.
 }
}



