BES2023 BES 2023 Section (29 abstracts)
Solving the puzzle of MEN2B syndrome in an adolescent girl
Nauwynck E 1 , Vanbesien J 1 , Gies I 1 , Ernst C 2 , Raeymaeckers S 3 , Verfaillie G 4 , Waelput W 5 , Vaeyens F 6 , De Grève J 6 , De Schepper J 1 & Staels W 1
1Vrije Universiteit Brussel (VUB), Universitair Ziekenhuis Brussel (UZ Brussel), Department of Pediatrics, Division of Pediatric Endocrinology, Brussels, Belgium; 2Vrije Universiteit Brussel (VUB), Universitair Ziekenhuis Brussel (UZ Brussel), Department of Radiology, Division of Pediatric Radiology, Brussels, Belgium; 3Vrije Universiteit Brussel (VUB), Universitair Ziekenhuis Brussel (UZ Brussel), Department of Radiology, Brussels, Belgium; 4Vrije Universiteit Brussel (VUB), Universitair Ziekenhuis Brussel (UZ Brussel), Department of Surgery, Brussels, Belgium; 5Vrije Universiteit Brussel (VUB), Universitair Ziekenhuis Brussel (UZ Brussel), Department of Anatomical pathology, Brussels, Belgium; 6Vrije Universiteit Brussel (VUB), Universitair Ziekenhuis Brussel (UZ Brussel), Centre for Medical Genetics, Brussels, Belgium
Introduction: MEN2B is a rare genetic tumor syndrome that causes medullary thyroid cancer at a young age and may lead to pheochromocytoma later in life. Early diagnosis is crucial for thyroidectomy before metastasis. This case report aims to increase awareness of MEN2B signs and symptoms and the need for early referral and treatment.
Case: A 10-year-old girl was referred for ultrasound imaging of a swollen submandibular gland that had been present for several months. In the past, she had been seen by an ENT specialist for a thickened upper lip present since birth, undergone surgery for clubfoot, and consulted several times for chronic constipation and poor weight gain. Ultrasound showed calcifications within the swollen submandibular gland and a nodule with calcifications in the right thyroid lobe, strongly suggestive of a thyroid neoplasm. In addition to the swollen left cervical gland, the patient’s examination revealed thickened lips (Figure 1A) and mucosal neuromas on the tongue (Figure 1B). Her thyroid gland appeared normal on palpation. She had an elongated face and thin body habitus. Thyroid hormone and serum thyroglobulin levels were normal, but serum calcitonin was markedly elevated at 11290 ng/l (ref. <7.2ng/l). Urinary catecholamines were within normal limits. Ultrasound-guided thyroid biopsies confirmed medullary thyroid cancer. A computed tomography scan of the lungs revealed two small nodules (< 1 cm) in the right lung. A positron emission tomography (PET) scan with Ga-DOTANOC showed heterogeneous uptake in the thyroid and some cervical lymph nodes but not in the pulmonary lesions. The patient underwent a total thyroidectomy with cervical lymph node dissection. The tumor had invaded several adjacent structures. Genetic analysis of lymphocytes and thyroid tissue revealed a pathogenic missense variant in the RET proto-oncogene in exon 16 (M918T), found in >95% of MEN2B patients. Calcitonin levels decreased after surgery but remained elevated at 5981 ng/l.
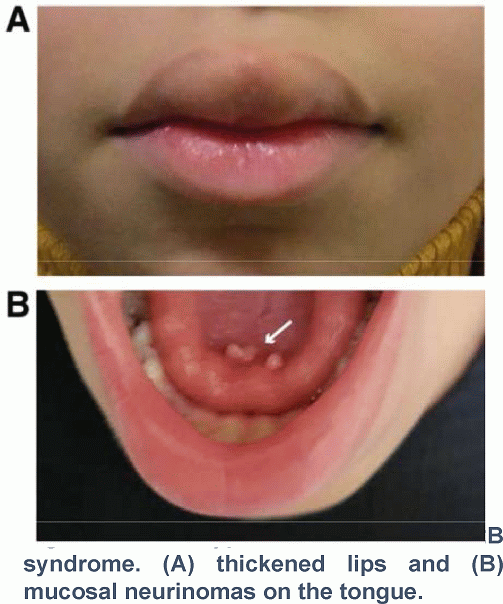
Figure 1. Phenotypical features of MEN2B syndrome. (A) thickened lips and (B) mucosal neurinomas on the tongue.
Conclusion: Medullary thyroid cancer in MEN2B is a highly aggressive disease. Clinical guidelines consistently recommend prophylactic thyroidectomy within the first few months of life. In this case, several diagnostic opportunities were missed despite the classic presentation of the disease. Early diagnosis and treatment could have resulted in a better prognosis, but this can only be achieved through increased awareness of this rare syndrome.Figure 1. Phenotypical features of MEN2B syndrome. (A) thickened lips and (B) mucosal neurinomas on the tongue.
 }
}



